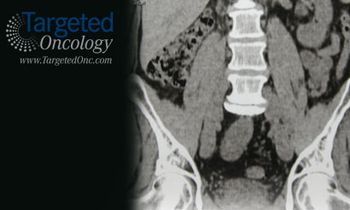
Controversy over optimal surveillance methods for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) continues to drive ongoing investigation into improved biomarkers and imaging techniques.

Controversy over optimal surveillance methods for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) continues to drive ongoing investigation into improved biomarkers and imaging techniques.
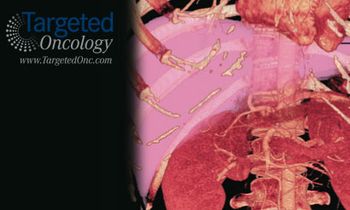
Although liver transplantation may be a more ideal treatment option compared with resection for many patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), donor availability remains a major limiting factor to its widespread incorporation.
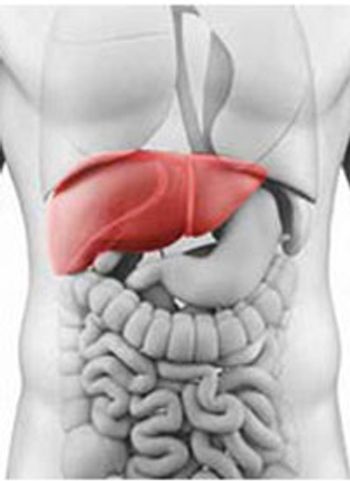
A novel, evidence-based model for staging liver function in the setting of hepatocellular carcinoma may offer improved guidance in the selection of appropriate, patient-specific therapeutic strategies.
A recent phase III clinical trial has offered hope for the prophylactic management of hand-foot skin reaction in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma treated with sorafenib.

The small molecule multikinase inhibitor sorafenib remains the only molecularly targeted therapy approved by the FDA for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma, with ongoing clinical trials diligently testing the potential for novel targeted agents or combination therapies to further improve patient outcomes in this setting.
Published: May 8th 2015 | Updated: April 18th 2020
Published: May 12th 2015 | Updated: April 18th 2020

Published: May 16th 2015 | Updated: April 18th 2020
Published: July 23rd 2015 | Updated: April 18th 2020
Published: July 23rd 2015 | Updated: April 18th 2020